Polling Information
Polling Tips
Poll cards and related information
Illustration on Guidance on Voting Procedure
Ballot Paper Design and Voting Validation and Counting Automation System
- Ballot Paper Design
- Voting Validation and Counting Automation System (“VVCAS”)
- Operation mechanism and advantages of the Optical Mark Recognition (“OMR”) technology
- Workflow for the use of OMR machines at Central Counting Station (“CCS”)
- Independent quality assurance services
Ballot Paper Design
(Front Side)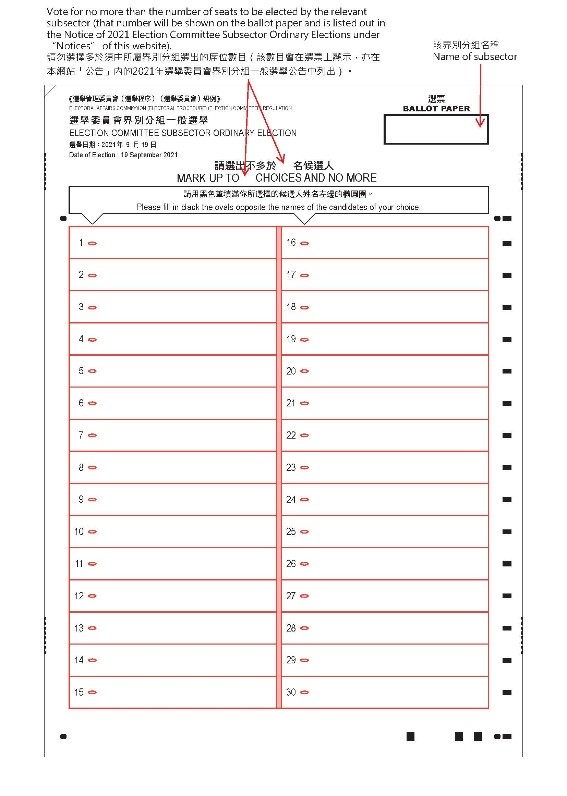
|
(Back Side)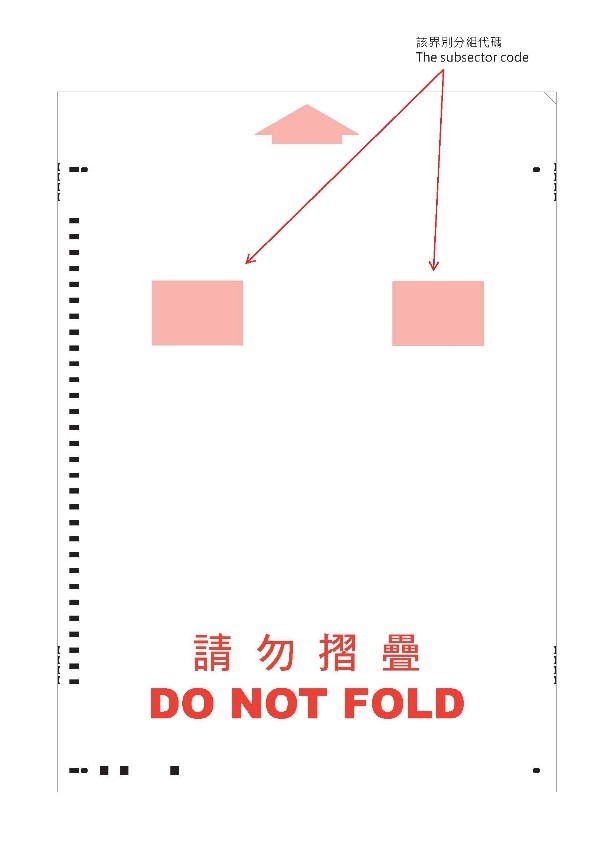
|
|---|
Voting Validation and Counting Automation System (“VVCAS”)
Given the large number of seats and candidates in the ECSSOEs and in line with the practice adopted since 1998, the Registration and Electoral Office (“REO”) has commissioned a contractor to update and enhance a VVCAS, whereby vote counting will be conducted in an automated mode with the aid of Optical Mark Recognition (“OMR”) machines.
The VVCAS makes use of the OMR technology to read the choices marked on ballot papers. It also allows manual input (i.e. Manual Key Entry, “MKE”) of the choices into the system.
The major components of the VVCAS include:
| Components | Functions |
|---|---|
|
1. Custom Programs of the VVCAS (“Custom Programs”) |
|
| 2. OMR machines |
|
| 3. MKE |
|
Operation mechanism and advantages of the OMR technology
- OMR is an optical technology using light beams to scan and capture data. After marking the designated areas on a form, the OMR technology will input the data into a computer system effectively and accurately in an automated mode, saving the tedious and repetitive manual efforts. In addition to reduction in operational cost, the chance of making mistakes during the manual input process can also be minimized significantly. Applications of the OMR technology include marking of multiple-choice examination papers, analysis of questionnaires and vote-counting for shareholders’ resolutions, etc.
- On counting of votes, an OMR machine will convert the marked choices on a ballot paper into digital format that can be processed by a computer counting system. When scanning a ballot paper, the OMR machine will emit beams of light to the ovals opposite the names of candidates. Since the marked ovals will reflect less light beams, through recognizing and measuring the light reflected, the OMR machine can identify and capture the votes on a ballot paper. The custom programs of the VVCAS will integrate, count and then store the data into the central database.
Workflow for the use of OMR machines at the CCS
- After the close of poll, Presiding Officers will deliver the ballot boxes to the CCS.
- After opening of the ballot boxes by ROs/Assistant ROs, he/she will instruct the counting staff to sort the ballot papers by subsectors. The sorted ballot papers will then be delivered to counting area of the respective Subsectors for grouping into three categories, i.e. “Clearly Invalid Ballot Papers”, “Questionable Ballot Papers” and “Ballot Papers Readable by OMR Machines”.
- “Ballot Papers Readable by OMR Machines” will be delivered to the Ballot Paper Scanning Zone for scanning of the votes by OMR machines.
- Ballot papers not accepted by the OMR machines will be submitted to the ROs for consideration. The validity of questionable ballot papers will be determined by the ROs at the Questionable Ballot Paper Determination Table in the presence of the candidates and their agents who are present. The determination result will also be announced there.
- Questionable ballot papers ruled as valid by ROs will be delivered to the MKE Zone for inputting the votes manually.
- Data input by the OMR machines and MKE will be integrated and counted by the VVCAS and then stored into the central database.
- Once a RO confirms that all vote-counting of the relevant subsector has been completed, he/she will inform the Command Centre. The Command Centre will print out the initial counting result through the VVCAS.
Independent quality assurance services
As in past elections, the REO will ensure that the 2021 ECSSOEs are conducted openly, fairly and honestly. Considering that the VVCAS is a vital part of the Elections, the REO has commissioned three independent quality assurance services to safeguard the reliability of the system:
- Quality Assurance Services
- To conduct comprehensive testing on the programs of the VVCAS, including function testing, system integration testing and load testing, etc.
- Computer Audit Services
- To provide a computer audit on the integrity of the entire automated counting process to ensure that the VVCAS complies with all relevant requirements, and monitor the integrity, security and accuracy of the data in the VVCAS.
- To audit the test plans, test specifications and test results submitted by both VVCAS Contractor and Quality Assurance Contractor, and offer advice where necessary.
- To monitor the whole counting process at the CCS.
- Information Technology Security Risk Assessment and Audit Services
- To provide an information technology security risk assessment and audit on the entire system, including access control, data security, application security, network and communication security, etc.
The contractors of the three independent quality assurance services have completed all pre-production testing on the VVCAS. Final system testing on the VVCAS will be conducted by the contractors at the CCS before its formal operation.
