|
|
Ballot Paper Design |
|
|
| |
Illustration on Guidance to Voters on the Voting Procedure |
|
|
| For details, please click here. |
| |
Voting Validation and Counting Automation System (“VVCAS”) |
|
Given the large number of seats and candidates for the Election Committee Subsector (“ECSS”) Ordinary Elections, in line with the practice in previous ECSS Ordinary Elections since 1998, the Registration and Electoral Office (“REO”) has commissioned a contractor to develop a VVCAS, whereby vote counting will be conducted in an automated mode with the aid of the Optical Mark Recognition (“OMR”) machines.
The VVCAS makes use of OMR technology to read the choices marked on the ballot papers and allows an alternative manual input mode (i.e. Manual Key Entry, “MKE”), to input the valid votes marked on those ballot papers which cannot be read by OMR.
The major components of the VVCAS include:
|
| Component |
Functions |
| 1. |
Custom Programs of the VVCAS
("Custom Programs") |
|
- Installed in the computers of relevant functional units at the Central Counting Station. It serves as the central platform operating the VVCAS.
- Storage of data for all contested Subsectors/Sub-subsectors (such as numbers of Election Committee members and candidates, candidates’ names and numbers).
- Integration and counting of all the valid votes on ballot papers inputted through OMR machines and MKE, and store them into the central database.
- Printing of vote counting related reports and election results.
|
|
|
- Scanning of ballot papers to record the valid votes into the VVCAS in an automated mode.
- Ballot papers rejected by the OMR machines will be delivered to the Returning Officers for consideration. Returning Officers will determine the validity of questionable ballot papers and announce their determinations at the Questionable Ballot Paper Determination Table in front of the candidates and agents who are present.
|
|
|
- For ballot papers which cannot be read by the OMR machines (e.g. questionable ballot papers determined by the Returning Officers as valid), the votes marked on them will be keyed into the VVCAS manually.
- To ensure the accuracy of data entered manually, each ballot paper will be inputted into the VVCAS by two counting staff members respectively and the VVCAS will instantly compare the results of the two entries. In case of any discrepancies, the VVCAS will give a prompt message which requires the counting staff to verify the data entered. The data inputted will only be stored into the VVCAS after all discrepancies have been reconciled.
|
|
| |
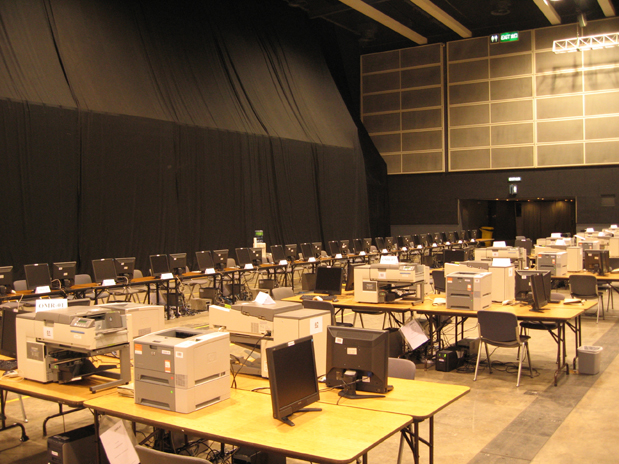

(Photo: The setting of OMR zone at the Central Counting Station in the past ECSS Elections)
|
| |
Operation mechanism and benefits of OMR technology
- OMR is an optical technology using light beams to scan and capture data. After users marked the designated areas on a form, the OMR technology can input the data into the computer effectively and accurately in an automated mode without the need of tedious and repetitive manual efforts. This not only reduces significantly the chance of making mistakes by manual input, but can also reduce operational costs. OMR technology has been developed for over 40 years and the areas of application include marking of multiple-choice examination papers, analysis of questionnaires, election-related applications, and the vote-counting for shareholders’ resolutions, etc.
- On the counting of votes, the OMR machine will convert the data on a ballot paper into digital information that can be processed by computer. When scanning a ballot paper, the OMR machine will emit beams of light to the ovals opposite the names of candidates. Since the marked ovals will reflect less light beams, through recognizing and measuring the light reflected, the OMR machine can identify and capture the votes on a ballot paper. The custom programs of VVCAS will integrate and count the data inputted, and store them into the central database.
|
Workflow for the use of OMR machine at Central Counting Station
- After the close of poll, Presiding Officers will deliver the ballot boxes to the Returning Officers at the Central Counting Station.
- After the opening of ballot box(es) by the Returning Officer, he/she will instruct the counting staff to sort the ballot papers according to different Subsectors/Sub-subsectors. The sorted ballot papers will then be delivered to the respective Subsectors/Sub-subsectors and subsequently be divided into three categories, namely “clearly invalid ballot papers”, “questionable ballot papers” and ““OMR readable” ballot papers”.
- “OMR readable” ballot papers will be delivered to the OMR zone. The OMR machines will scan and read the votes on the ballot papers and print out the relevant counting reports.
- All ballot papers rejected by the OMR machines will be delivered to the Returning Officers for consideration. For questionable ballot papers, Returning Officers will announce their determinations at the Questionable Ballot Paper Determination Table in front of the candidates and their agents.
- Questionable ballot papers accepted by the Returning Officers will be delivered to the MKE zone for inputting the votes on them manually.
- Data inputted by the OMR machines and the MKE will be integrated and counted by the VVCAS and then stored into the central database.
- Once a Returning Officer confirms that all vote-counting of the relevant Subsector/Sub-subsector has been completed, he/she will inform the Command Post. The Command Post will print out the initial counting result through the VVCAS.
|
Points to note in marking ballot papers
To ensure OMR machines can accurately read the choice(s) marked on a ballot paper, voters should pay attention to the following points: |
| Points to note when marking a ballot paper |
Purpose |
| 1. |
Use the black pen provided at the polling station to mark the ballot paper. |
|
To ensure the votes marked can be accurately read by the OMR machine.
|
| 2. |
When marking the ballot paper, the voter should follow the instructions printed on the ballot paper to shade the ovals opposite the names of the candidates of his/her choice.
 |
(for reference only) |
|
|
To ensure that OMR machine can accurately read all choices marked on ballot papers.
|
| 3. |
Put the marked ballot paper into the envelope provided at the polling station and put them into the ballot box.
 |
(for reference only) |
|
|
To keep the ballot paper intact for smooth OMR scanning.
|
|
|
| Contingency measures |
- In case the number of candidates for any Subsector/Sub-subsector exceeds the maximum number of candidates an OMR readable ballot paper can accommodate, the REO will resort to the MKE mode whereby valid votes recorded on the ballot papers will be manually inputted into the VVCAS.
- Inputting all votes on the valid ballot papers requires longer time and sufficient counting staff. To cater for this possibility, the REO will train up sufficient counting staff to ensure the smooth conduct of vote counting.
|
| |
| Independent quality assurance services |
|
As in past elections, the REO will ensure that the 2016 ECSS Ordinary Elections are conducted openly, fairly and honestly. Considering that the VVCAS is the vital part of the Elections, the REO has commissioned three independent quality assurance services to ensure the integrity and reliability of the VVCAS:
|
(i) Quality Assurance Services
- To conduct comprehensive testing on the programs of the VVCAS, including function testing, system integration testing, and load testing, etc.
- Quality Assurance Contractor is like a quality control officer in a production line and it is tasked to test whether the quality of the product meets the required standard.
|
(ii) Computer Audit Services
- To provide a computer audit on the integrity of the entire automated counting process so as to ensure the VVCAS complies with all relevant requirements, and monitor the integrity, security and accuracy of the data in the VVCAS.
- To audit the test plans, test specifications and test results submitted by both VVCAS Contractor and Quality Assurance Contractor, and offer advice where necessary.
- To monitor the whole counting process at the Central Counting Station.
- Computer Audit Contractor is like a work supervisor in a production line who oversees the workflow of the production so as to ascertain every step in the operation complies with the standard procedures.
|
(iii) Information Technology Security Risk Assessment and Audit Services (“IT SRAA”)
- To provide an IT security risk assessment and audit on the entire system, including security management, physical security, access control, data security, application security, network and communication security, etc.
- IT SRAA Contractor is like a security officer in the production line who is responsible to keep its overall safety and to ensure that the production system will be free from security breaches.
|
|
The contractors of the three independent quality assurance services have completed all pre-production testing on the VVCAS. Final system testing on the VVCAS will be conducted by the contractors at the production site at the Central Counting Station before formal operation of the Central Counting Station.
|
Back to Top |



